MPEG to M4VMPEG to M4V Converter, Convert MPEG to M4V |
 |
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact |
Total Video Audio Converter converts MPEG to M4V with high quality easily. The converter supports MPEG-4 and H.264 codecs for M4V file. With the MPEG to M4V conversion software, you could set bit rate, frame rate, video size, aspect ratio, etc. By default, the software calculates bit rate for result M4V file according to original video size automatically. As large video size needs bigger bit rate. Besides M4V, the converter converts MPEG to popular formats and portable devices such as PSP, PS3, WebM, 3G2, iPod, FLV, iPad, ASF, MPG, Xvid, and so on. The software also other video and audio formats, for example, TS to iPad, WMV to Xbox 360, MP4 to Xbox 360, M4V to FLV, M2TS to FLV, 3G2 to VOB, DVD to 3GP, H.263 to WMV, and so on. MPEG to M4V conversion software could convert file in batch. And, it's full compatible with 32-bit and 64-bit Windows 7.
What is MPEG? The MPEG standards consist of different Parts. Each part covers a certain aspect of the whole specification. The standards also specify Profiles and Levels. Profiles are intended to define a set of tools that are available, and Levels define the range of appropriate values for the properties associated with them. MPEG has standardized the following compression formats and ancillary standards:
In addition, the following standards, while not sequential advances to the video encoding standard as with MPEG-1 through MPEG-4, are referred to by similar notation:
Moreover, relatively more recently than other standards above, MPEG has started following international standards; each of the standards holds multiple MPEG technologies for a way of application. For example, MPEG-A includes a number of technologies on multimedia application format.
What is M4V? Apple uses M4V files to encode TV episodes, movies, and music videos in the iTunes Store. The copyright of M4V files may be protected by using Apple's FairPlay DRM copyright protection. To play a protected M4V file, the computer needs to be authorized (using iTunes) with the account that was used to purchase the video. However, unprotected M4V files without AC3 audio may be recognized and played by other video players by changing the file extension from '.m4v' to '.mp4'. Besides Apple iTunes and Apple QuickTime Player, M4V files can also be opened and played with the version of Windows Media Player included with Windows 7, Media Player Classic, RealNetworks RealPlayer, VideoLAN VLC media player and Nero Showtime (included with Nero Multimedia Suite). The format, with DRM removed, can also be played in the webOS Video Player for use on the Palm Pre, Palm Pixi smartphones. It is also playable by the Android operating system with its video player. It can also be played with the BS Player Pro. M4V video with FairPlay attached to it is read in QuickTime as AVC0 Media. Step-by-Step Instructions to Converting MPEG to M4V
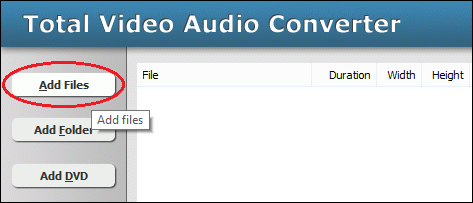 Click "Add Files" to choose MPEG files and add them to conversion list. 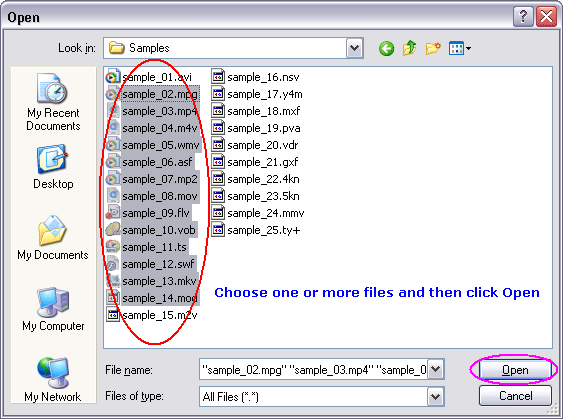 Choose one or more MPEG files you want to convert and then click Open.  [Optional, for advanced user] If you want to change M4V encoding parameters, for example, vodec codec, bit rate, frame rate, video size, and aspect ratio, please click "Options". 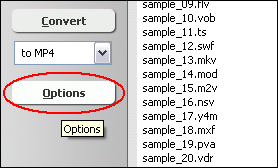  [Optional] Switch to tab "Video & Audio" and then choose "M4V" at "Output Format", and then set encoding parameters.  Click "Convert" to convert MPEG files to M4V. 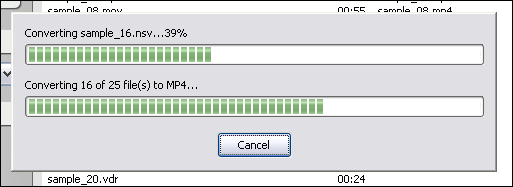 The software is converting MPEG to M4V. 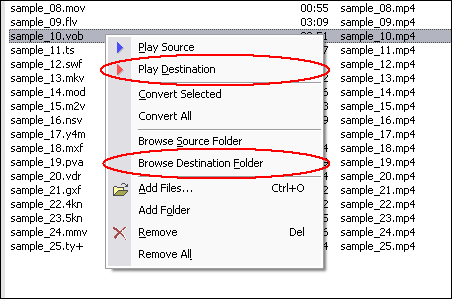 When conversion completes, you can right-click converted item and choose "Play Destination" to play the outputted M4V file; or choose "Browse Destination Folder" to open Windows Explorer to browse the outputted M4V file. MPEG to M4V Conversion Software is 100% clean and safe to
install. It's certified by major download sites. Convert MPEG to M4V Related Topics:
|
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact | Links |
| Copyright © 2008-2017 Hoo Technologies All rights reserved. Privacy Policy |

