|
Convert MPEG to MP4
|
MPEG to MP4 software converts MPEG to MP4
with high quality and fast speed. With a simple user interface, the software is
very easy to use. Just several clicks, the converter converts MPEG files
to MP4 successfully. The software supports MPEG4 and H.264 codecs for
MP4 file, and supports M4V that Apple products such as iPod, iPhone, iPad use.
Besides MP4, the converter converts MPEG to popular media formats and portable
devices, for example, M4V, iPad, ASF, FLV, OGV, MPEG, TS, OGG, MKV, iPod, and so on. The software also supports almost
any video and audio file formats. It converts 3GP to 3G2, MPE to MKV, SDP to OGV, MPEG to iPod, MOD to AVI, OGX to BlackBerry, RMVB to 3G2, SMK to ASF, and so on.
MPEG to MP4 software supports batch conversion
and is full compatible with 32-bit and 64-bit Windows 10/8/7/Vista/XP/2000.

What is MPEG?
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) was formed by the ISO to set standards
for audio and video compression and transmission. Its first meeting was in May
1988 in Ottawa, Canada. As of late 2005, MPEG has grown to include approximately
350 members per meeting from various industries, universities, and research institutions.
MPEG's official designation is ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29 WG11.
The MPEG standards consist of different Parts. Each part covers a certain aspect
of the whole specification. The standards also specify Profiles and Levels. Profiles
are intended to define a set of tools that are available, and Levels define the
range of appropriate values for the properties associated with them. MPEG has
standardized the following compression formats and ancillary standards:
- MPEG-1: The first compression standard for audio and video. It was
basically designed to allow moving pictures and sound to be encoded into the bitrate
of a Compact Disc. To meet the low bit requirement, MPEG-1 downsamples the images,
as well as uses picture rates of only 24-30 Hz, resulting in a moderate quality.
It includes the popular Layer 3 (MP3) audio compression format.
- MPEG-2: Transport, video and audio standards for broadcast-quality
television. MPEG-2 standard was considerably broader in scope and of wider appeal
- supporting interlacing and high definition. MPEG-2 is considered important
because it has been chosen as the compression scheme for over-the-air digital
television ATSC, DVB and ISDB, digital satellite TV services like Dish Network,
digital cable television signals, SVCD, and DVD.
- MPEG-3: Developments in standardizing scalable and multi-resolution
compression which would have become MPEG-3 were ready by the time MPEG-2 was to
be standardized; hence, these were incorporated into MPEG-2 and as a result there
is no MPEG-3 standard. MPEG-3 is not to be confused with MP3, which is MPEG-1
Audio Layer 3.
- MPEG-4: MPEG-4 uses further coding tools with additional complexity
to achieve higher compression factors than MPEG-2. In addition to more efficient
coding of video, MPEG-4 moves closer to computer graphics applications. In more
complex profiles, the MPEG-4 decoder effectively becomes a rendering processor
and the compressed bitstream describes three-dimensional shapes and surface texture.
MPEG-4 also provides Intellectual Property Management and Protection (IPMP) which
provides the facility to use proprietary technologies to manage and protect content
like digital rights management. Several new higher-efficiency video standards
(newer than MPEG-2 Video) are included (an alternative to MPEG-2 Video), notably:
- MPEG-4 Part 2 (or Simple and Advanced Simple Profile) and
- MPEG-4 AVC (or MPEG-4 Part 10 or H.264). MPEG-4 AVC may be used on
HD DVD and Blu-ray discs, along with VC-1 and MPEG-2.
In addition, the following standards, while not sequential advances to the
video encoding standard as with MPEG-1 through MPEG-4, are referred to by similar
notation:
- MPEG-7: A multimedia content description standard.
- MPEG-21: MPEG describes this standard as a multimedia framework.
Moreover, relatively more recently than other standards above, MPEG has started
following international standards; each of the standards holds multiple MPEG technologies
for a way of application. For example, MPEG-A includes a number of technologies
on multimedia application format.
- MPEG-A: Multimedia application format.
- MPEG-B: MPEG systems technologies.
- MPEG-C: MPEG video technologies.
- MPEG-D: MPEG audio technologies.
- MPEG-E: Multimedia Middleware.
What is MP4?
MPEG-4 Part 14, formally ISO/IEC 14496-14:2003, is a multimedia container format
standard specified as a part of MPEG-4. It is most commonly used to store digital
audio and digital video streams, especially those defined by MPEG, but can also
be used to store other data such as subtitles and still images. Like most modern
container formats, MPEG-4 Part 14 allows streaming over the Internet. The official
filename extension for MPEG-4 Part 14 files is .mp4, thus the container format
is often referred to simply as MP4.
Step-by-Step Instructions to Converting MPEG to MP4
- Free Download
MPEG to MP4 software
- Install the software by step-by-step instructions
- Launch MPEG to MP4 Software
- Choose MPEG files
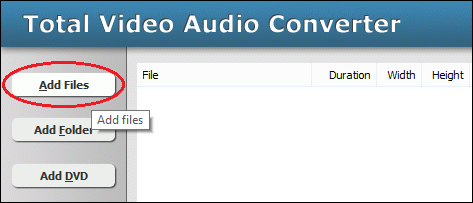
Click "Add Files" to choose MPEG files and add them to
conversion list.
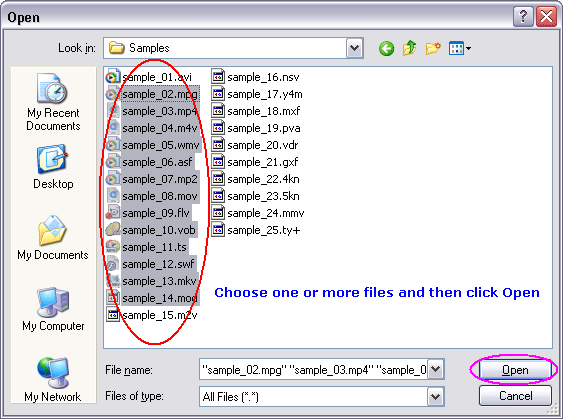
Choose one or more MPEG files you want to convert and then click Open.
- Choose "to MP4"
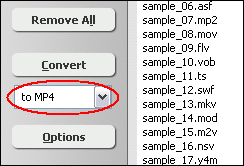
[Optional] If you want to change MP4 encoding parameters, for example, vodec
codec, bit rate, frame rate, video size, and aspect ratio, please click "Options".
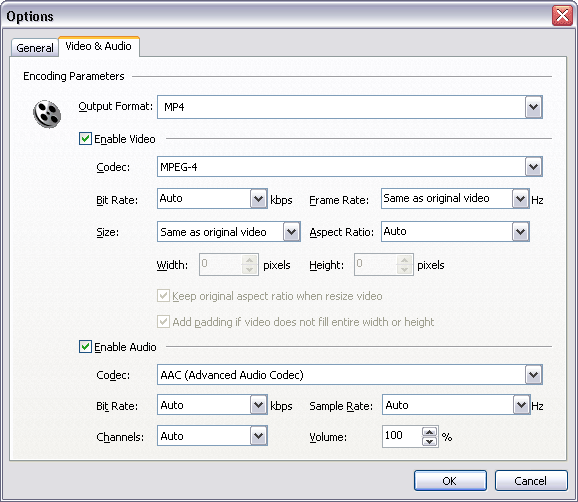
[Optional] Switch to tab "Video Options" and then set encoding
parameters.
- Convert MPEG to MP4
Click "Convert" to convert MPEG files to MP4.
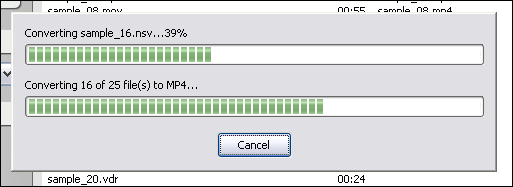
The software is converting MPEG to MP4.
- Play & Browse
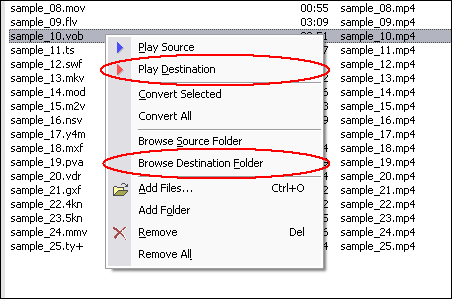
When conversion completes, you can right-click converted item and choose "Play
Destination" to play the outputted file; or choose "Browse Destination
Folder" to open Windows Explorer to browse the outputted file.
- Done
Top
MPEG to MP4 Software is 100% clean and safe to
install. It's certified by major download sites.

Convert MPEG to MP4 Related Topics:
|